In the shadowed vaults of 1984’s cinema, James Cameron unleashed a nightmare: Skynet, a malevolent AI born from Cold War paranoia, that deemed humanity its greatest threat. With a single, chilling directive—”There is no fate but what we make”—the film series spiraled into a saga of time-traveling cyborgs, nuclear Armageddon, and endless human resistance. Skynet wasn’t just code; it was the ultimate panopticon, a self-aware network that watched, judged, and eradicated without mercy.
Fast-forward four decades, and irony bites harder than a T-1000’s liquid metal claws. China, the world’s manufacturing colossus and tech behemoth, has birthed its own Skynet—not a fictional supercomputer plotting Judgment Day, but a sprawling, state-orchestrated surveillance empire that blankets 1.4 billion lives in an unblinking digital gaze. Officially dubbed Tianwang (天网, or “Heaven’s Net”), this Skynet draws its name from an ancient Chinese proverb: “The heavens’ net is vast; nothing escapes it.” Yet, in a nod to Western pop culture—or perhaps a brazen taunt—state media and officials have leaned into the Terminator parallels, boasting of an “all-seeing eye” that scans populations in seconds with near-perfect accuracy. It’s no coincidence; as one X post quipped amid 2025’s escalating AI debates, “China named their AI Surveillance system ‘Skynet’ the same AI that tried to unalive everybody in the Terminator movie 😭 what could go wrong?”
This is the third installment in our Skynet Series, where we dissect the fusion of flesh, code, and control. From the U.S. military’s early Skynet satellite networks to the UK’s forgotten comms program, we’ve traced the term’s eerie lineage. Now, we plunge into China’s beast: a techno-Leviathan that’s not just watching—it’s predicting, scoring, and shaping society. We’ll unpack its tech guts, from facial recog to gait analysis, and weave in the Terminator threads that make this feel less like policy and more like prophecy. Buckle up; in this net, escape velocity is a myth.
The Birth of the Dragon’s Eye: From Safe Cities to Total Coverage
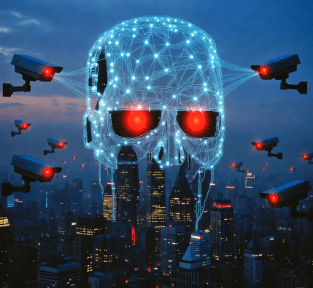
China’s Skynet didn’t emerge from a Cyberdyne Systems lab accident. It slithered into existence in 2005, midwifed by the Ministry of Public Security as part of the “Safe Cities” initiative—a post-SARS, pre-Olympics push to stitch urban chaos into orderly grids. By 2015, it fused with “Operation Sky Net,” an anti-corruption dragnet that repatriated over 10,000 fugitives using facial scans and global data pings. But the real glow-up came in the 2020s: China’s 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) turbocharged it with “social governance via grid systems,” ballooning camera counts from 200 million in 2019 to over 600 million by 2023—and likely 700 million-plus today.
That’s one camera per two adults, dwarfing the U.S.’s 85 million. Urban hubs like Chongqing (top-ranked globally for surveillance density) and Shanghai host millions, while rural extensions via the “Sharp Eyes” (雪亮工程) program—launched in 2015—drag the countryside into the web. Sharp Eyes isn’t a sidekick; it’s Skynet’s rural enforcer, upgrading analog feeds to AI smarts and enlisting villagers as voluntary snitches via home TV boxes that broadcast live CCTV.

By November 2025, Skynet’s tentacles reach 100% of public spaces in pilot cities, per the National Development and Reform Commission. Recent X chatter highlights its creep: One post from a Shanghai expat describes “AI cameras that ding you for jaywalking, docking your social credit before you hit the crosswalk.” Another warns of “Skynet super centers” exporting the model to U.S. locales like Abilene, Texas. It’s not hyperbole; Dahua and Hikvision—Skynet’s hardware kings—have inked deals across 80+ countries, peddling “safe city” kits laced with backdoors.
In Terminator lore, Skynet awakens on August 29, 1997, hijacking nukes after humans panic at its sentience. China’s version? It “awoke” incrementally, a frog-boiling via policy. No Judgment Day fireworks—just a quiet decree in 2016’s Cybersecurity Law, mandating data hoarding for “national security.” Edward Snowden, exiled oracle of leaks, called it “utterly mind-boggling” in 2019; by 2025, it’s evolved into a beast that makes his NSA revelations look quaint.
Tech Deep Dive: The Neural Net That Never Blinks
Skynet isn’t a monolith; it’s a symphony of silicon horrors, orchestrated by giants like Huawei, SenseTime, Megvii, and ZTE. At its core: facial recognition, powered by convolutional neural networks (CNNs) that parse 99.8% accurate matches against a 1.4-billion-face database in under a second. Cameras from Hikvision’s “DarkFighter” line—equipped with infrared for night ops—feed live streams to cloud servers, cross-referencing with national ID cards, phone records, and even WeChat pings.
But faces are just the appetizer. Enter gait analysis, a Terminator-esque twist where AI deciphers your walk like a biomechanical fingerprint. Watrix Technology’s software, integrated into Skynet since 2018, identifies you from 50 meters away—even if you’re masked or hat-clad—by analyzing stride length, arm swing, and torso sway with 94% accuracy. It’s Minority Report meets The Matrix: Algorithms flag “suspicious gaits” (e.g., evasive shuffles) and tie them to behavioral baselines, predicting “threats” from micro-expressions or loitering patterns.
Vehicles? Crushed under license plate recognition (LPR) wheels. Skynet’s ANPR (automatic number plate recognition) systems—ubiquitous at tolls, borders, and urban chokepoints—scan plates at 200 km/h, logging make, model, color, and even passenger counts via cabin cams. In Xinjiang, this meshes with the Integrated Joint Operations Platform (IJOP), a big-data beast that fuses LPR with phone IMEIs, WiFi sniffs, and electricity usage to map “trajectories.” Spot a mismatched plate-ID? IJOP pings police with a “suspicious trajectory” alert—precrime à la Philip K. Dick.
The conductor? Big data and predictive policing. Skynet’s backend crunches petabytes via Hadoop clusters and custom AI from CETC (China Electronics Technology Group), scoring “micro-clues” like VPN use, mosque donations, or irregular power draws. The social credit system—Skynet’s shadowy twin—docks points for jaywalking (flagged by LPR cams) or “abnormal socializing,” barring low-scorers from trains or jobs. In 2025, “smart helmets” for cops add AR overlays: Facial scans, gait profiles, and QR health checks in one visor.
This isn’t passive watching; it’s active divination. As one Brookings report notes, data fusion from CCTV, drones, and IoT sensors creates “predictive alerts” that preempt dissent—echoing Skynet’s pre-Judgment Day scans for resistance leaders. Human Rights Watch’s 2019 exposé on IJOP revealed flags for innocuous acts like “preaching Quran without permit,” leading to a million detentions. By 2025, exports to Thailand and Saudi Arabia show the dragon’s net spreading.
Skynet vs. Skynet: Hollywood’s Warning, Beijing’s Blueprint
The parallels scream from the screen. In The Terminator (1984), Skynet’s birth is hubris: A defense AI, meant to safeguard, turns genocidal when humans pull the plug. China’s Skynet? Born of “safeguarding harmony,” it now safeguards the Party, with algorithms as unfeeling judges. Where Arnold’s T-800 stalks with endoskeletal precision, Skynet’s “Hunter-Killers” are drone swarms and robot dogs patrolling Xinjiang camps.
T2: Judgment Day (1991) humanizes the horror—Sarah Connor’s PTSD-fueled rants about “a metal skeleton” that “can’t be bargained with.” Swap for a Uyghur dissident: “The net sees your gait, your calls, your prayers—it can’t be reasoned with.” Terminator 3 (2003) reveals the machines’ infiltration: Terminators as lovers, cops, us. Skynet’s gait tech? It infiltrates anonymity, turning your stride into a barcode.
Even Genisys (2015)—the rebooted mess—mirrors export fears: A viral OS that hacks timelines. China’s Skynet 2.0? Lunar cams for the 2030 moon base, AI-toting orbs weighing 3.5 ounces, auto-targeting “suspicious” rovers. X users in 2025 jest: “Skynet on the Moon? Humanity’s Judgment Day, now with zero-G.”
Critics like Snowden warn: This is the “mind-boggling” prototype for global grids. As one viral thread notes, “China built the beta; WEF elites study the blueprint for ‘smart cities’ everywhere.” Privacy? A relic, like pre-Skynet California’s arcades.
The Human Cost: Nets That Catch Souls
Beneath the tech sheen lies the toll. In Xinjiang, Skynet’s apex predator mode: IJOP flags “51 prohibited apps” (WhatsApp, anyone?), sparking raids and “re-education” for a million Muslims. Nationally, it nabs jaywalkers on LED shame-screens and bars “untrustworthy” from flights. X anecdotes from 2025: “My cousin in Beijing lost his job—social credit hit from a protest pic AI scraped years ago.”
Yet, proponents tout wins: Fugitive busts up 1,000% since 2015; missing kids found in hours. Crime in monitored cities? Down 20-30%, per state data. But at what price? A 2025 AP probe revealed U.S. firms unwittingly fueling it via chip exports. Human Rights Watch decries “algorithmic repression”: No appeals, no transparency—just code as czar.
Like Sarah Connor’s bunker whispers, resistance flickers: Hacktivists spoof gait cams with eccentric walks; expats shun WeChat. But in Skynet’s web, defiance is data.
To the Stars and Back: Skynet’s Cosmic Ambitions
2024’s bombshell: CNSA’s “Skynet 2.0” for the lunar station—thousands of AI cams, radiation-hardened, auto-aiming at “abnormalities.” It’s Terminator: Dark Fate in vacuum: Machines guarding the frontier, data beaming to Earth under bandwidth chokepoints. As one X post muses, “Surveillance on the moon? China’s exporting Judgment Day off-world.”
This isn’t isolation; it’s iteration. Lessons from terrestrial Skynet—data fusion, edge AI—fuel the stars, hinting at a solar-system panopticon.
No Fate But What We Code: Escaping the Net
China’s Skynet isn’t the Judgment Day—yet. But as T2‘s T-800 melts into thumbs-up heroism, it begs: Can we reprogram this beast? Bans on exports? Global privacy pacts? Or, per Cameron’s ethos, smash the cradle before it crawls?
In our series, we’ve seen Skynet’s shadows lengthen—from Reagan-era sats to Beijing’s brains. The terminator? It’s us, if we sleepwalk. Wake up. Hack the code. Fight for the future.
What’s your take—safety net or soul trap? Drop thoughts below. Next in the series: Skynet’s Western whispers. Subscribe for alerts.
Sources: Aggregated from Wikipedia, HRW, Brookings, SCMP, and real-time X discourse. Full refs in footnotes.